Stephen Gray was pursuing a long series of experiments with electricity. In producing charge on a long glass tube, he discovered in 1729 that he could communicate the electrical effect to other objects by direct connection. Using string, he could charge an object over 50 feet from the rubbed tube, but oddly enough some other substances, such as silk thread, would not carry charge. Brass wire would transmit charge even better. These experiments with charged strings and glass tubes revealed the properties of conduction, insulation, and transmission.
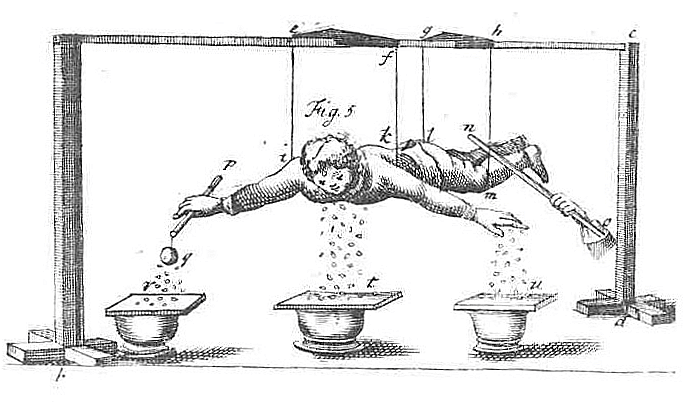
The depiction above shows one of Gray’s most famous experiments, in which he showed that a boy suspended by (insulating) silk cords could be charged (with the glass tube) and then as a (conducting) body could (electrostatically) attract small objects. Dramatic experiments such as these became quite well-known. Finally, after Newton’s death in 1732, Gray was admitted as a member of the Royal Society in recognition of his efforts, but he died destitute a few years later in 1736. [via]
[Image found here.]